Anxiety In Nigeria As Presidential Tribunal Delivers Ruling In Live Broadcast
Everything will be at a standstill in Nigeria on Wednesday, the day the Justice Haruna Tsammani-led five-member Presidential Election Petition Court, PEPC, sitting in Abuja delivers its judgement on the three petitions that are seeking to nullify President Bola Tinubu’s election.
On this day, the court, according to its Chief Registrar, Umar Bangari would permit a live broadcast of its judgement on the three petitions to ensure transparency and openness in its proceedings.
Nigerians have eagerly awaited this day following the wrangling that followed the February 25 presidential elections that had drawn petitions, marked: CA/PEPC/03/2023, CA/PEPC/05/2023 and CA/PEPC/04/2023, from the candidates of the Labour Party, LP, Peter Obi; a former Vice President and candidate of the Peoples Democratic Party, PDP, Atiku Abubakar; as well as the Allied Peoples Movement, APM, respectively.
The Justice Haruna Tsammani-led five-member panel of the court had on August 1, okayed the cases for judgement, after all the parties adopted their final briefs of argument.
On the day, however, “Access to the court premises will be strictly on accreditation. Only accredited individuals, including counsel and representatives of political parties, will be granted access to the courtroom, according to Bangari who advised “Interested members of the public are advised to watch proceedings from their television sets”.
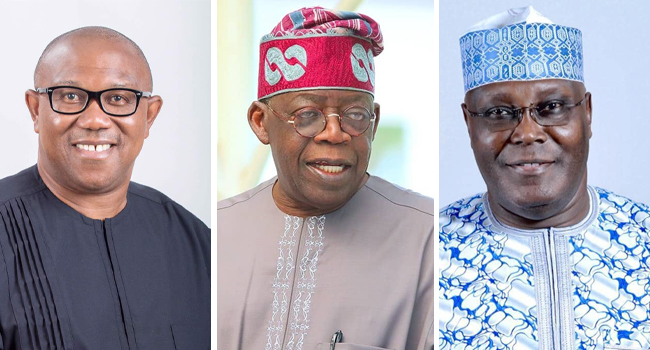
The Independent National Electoral Commission, (INEC), on March 1, announced that Tinubu of the ruling All Progressives Congress, APC, scored a total of 8,794,726 votes to defeat the two major contenders, Atiku of the PDP, who came second with a total of 6,984,520 votes, and, Obi of the LP, who came third with a total of 6,101,533 votes in the presidential election of February 25, ahead of 17 other candidates that participated in the contest.
Not satisfied with the declaration, both Obi and Atiku in their separate petitions, claimed they won the presidential poll, even as they challenged Tinubu’s eligibility to contest the election.
The petitioners, aside from praying the court to declare that President Tinubu did not secure the majority of lawful votes that were cast at the election, equally sought the withdrawal of the Certificate of Return that was issued to him by INEC.
Alternatively, they prayed the court to order a fresh presidential election, with the exclusion of President Tinubu whom they argued was ab initio, not qualified to participate in the poll.
The Electoral Act 2022 makes it mandatory for aggrieved candidates to file a petition within 21 days after the result is declared by INEC, file a petition before the court which shall deliver its judgement in writing within 180 days.
The court had on July 5, concluded its hearing of both Atiku and Obi’s petitions
While Obi closed his case after he called 13 witnesses who testified and tendered several documentary exhibits, Atiku, produced 27 witnesses and equally tendered exhibits before the court.
On their part, both INEC and President Tinubu wrapped up their defence in both cases with one witness each, while the APC failed to produce any witness before the court.
However, all the Respondents, in their respective written addresses, urged the court to dismiss all the petitions for want of merit.
They argued that the petitioners were unable to discharge the burden of proof that was placed on them by the law.
According to the Respondents, whereas the petitioners raised allegations that had elements of crime in them, they, however, failed to prove them beyond reasonable doubt as required by the law.
President Tinubu urged the court to hold that he was validly returned as winner of the election, by the INEC.
Specifically, Atiku, in the joint petition he filed with his party, maintained that the declaration of Tinubu as winner of the presidential election was “invalid because of non-compliance with the provisions of the Electoral Act, 2022”, insisting that he “was not duly elected by a majority of lawful votes cast at the election”.
He told the court that Tinubu, who was cited as the 2nd Respondent, “was at the time of the election not qualified to contest.”
In a further process he filed through his team of lawyers led by Chief Chris Uche, SAN, Atiku told the court that the President-elect had “demonstrated inconsistency as to his actual date of birth, secondary schools he attended (Government College Ibadan); his State of origin, gender, actual name; certificates evidencing Universities attended (Chicago State University).”
“The purported degree Certificate of the 2nd Respondent allegedly acquired at the Chicago State University did not belong to him but to a female (F) described as “F” in the Certificate bearing the name Bola Tinubu.
“The 2nd Respondent did not disclose to the 1st Respondent (INEC) his voluntary acquisition of the citizenship of the Republic of Guinea with Guinean Passport No. D00001551, in addition to his Nigerian citizenship. The 2nd Respondent is hereby given notice to produce the original copies of his said two passports,” Atiku added.
He argued that the APC candidate did not meet the constitutional threshold and “is constitutionally disabled from contesting for the office of President of the Federal Republic of Nigeria”.
Likewise, Obi and LP, in their petition, argued that at the time Tinubu’s running mate, Senator Kashim Shettima, became the Vice Presidential candidate, he was still the nominated candidate of the APC for the Borno Central Senatorial election.
They equally challenged Tinubu’s eligibility to contest the presidential election, alleging that he was previously indicted and fined the sum of $460,000.00 by the United States District Court, Northern District of Illinois, Eastern Division, in Case No: 93C 4483, for an offence involving dishonesty and drug trafficking.
On the ground that the election was invalid because of corrupt practices and non-compliance with the provision of the Electoral Act, 2022, the petitioners argued that INEC acted in breach of its Regulations and Guidelines.
The Petitioners contended that the electoral body was in the course of the conduct of the presidential poll, mandatorily required to prescribe and deploy technological devices for the accreditation, verification, continuation and authentication of voters and their particulars as contained in its Regulations.
Consequently, they prayed the court to not only hold that Tinubu was not qualified to contest the election but to also declare that all the votes recorded for him were wasted votes owing to his non-qualification/disqualification.
“That it is determined that based on the remaining votes (after discountenancing the votes credited to the 2nd Respondent) the 1st Petitioner (Obi) scored a majority of the lawful votes cast at the election and had not less than 25% of the votes cast in at least 2/3 of the States of the Federation, and the Federal Capital Territory, Abuja, and satisfied the constitutional requirements to be declared the winner of the 25th February 2023 presidential election.
“That it be determined that the 2nd Respondent having failed to score one-quarter of the votes cast at the presidential election in the Federal Capital Territory, Abuja, was not entitled to be declared and returned as the winner of the presidential election held on 25th February, 2023.
In the alternative, the petitioners want an order cancelling the election and compelling INEC to conduct a fresh election in which Tinubu, Shettima and the APC, listed as 2nd, 3rd and 4th Respondents, respectively, shall not participate.
They urged the court to declare that since Tinubu was not duly elected by a majority of the lawful votes cast in the election, therefore, his return as the winner of the presidential election, was unlawful, unconstitutional and of no effect whatsoever.
In a further alternative prayer in the petition dated March 20, which Obi filed through a team of lawyers led by Dr Livy Uzoukwu, SAN, and Awa Kalu, SAN, he wants the tribunal to hold that the presidential election was void on the ground that it was not conducted substantially by the provisions of the Electoral Act 2022, and the 1999 Constitution, as amended.
Likewise, an order, “cancelling the presidential election conducted on 25th February 2023 and mandating the 1st Respondent to conduct a fresh election for the President, the Federal Republic of Nigeria.”
Though five petitions were initially filed to nullify Tinubu’s election, however, the Action Alliance, AA, on May 8, withdrew its case, even as the Action Peoples Party, APP, followed suit two days later by also discontinuing further proceedings on its petition.
The Allied Peoples Movement, APM, which refused to withdraw its petition, had on July 14, adopted its final written address, even as the court reserved its judgment on the petition.
The APM, in its petition, argued that the withdrawal of Mr. Ibrahim Masari who was initially nominated as the Vice-Presidential candidate of the All Progressives Congress, APC, invalidated Tinubu’s candidacy given Section 131(c) and 142 of the 1999 Constitution, as amended.
The party argued that there was a gap of about three weeks between the period that Masari, who was listed as the 5th Respondent in the petition, expressed intention to withdraw, the actual withdrawal of his purported nomination, and the time Tinubu purportedly replaced him with Senator Kashim Shettima.
It further argued that Tinubu’s candidature had elapsed at the time he nominated Shettima as Masari’s replacement.


Comments are closed.